Quantification of carbon nanotubes in polymer composites†
Abstract
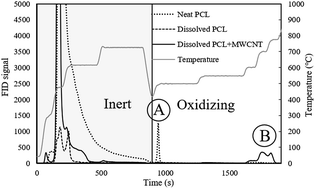
Quantifying carbonaceous nanomaterials (CNMs) has largely been limited to soil, water or biological matrices, but the largest application of CNMs is carbon nanotubes (CNTs) embedded in polymers or plastics. This study introduces a two-step analytical method that matches solvents to dissolve a broad range of polymers, with a subsequent programmed thermal analysis (PTA) quantification technique. Hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) and chloroform dissolved the broadest range of polymers containing CNMs. Subsequent PTA could accurately detect and quantify multi-walled (MWCNT) or single-walled (SWCNT) carbon nanotubes at an absolute amount of 0.2 μg (0.2 ppm (m m−1) for a 1 g sample) at a high reproducibility (<20% standard deviation). Lower detection limits can be obtained by using larger sample sizes. For SWCNTs with high metal catalyst concentration, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was demonstrated as secondary confirmational analytical technique. In that case, the CNM concentration was determined based on the specific metal in CNMs detected by ICP-MS. The result was comparable to the two-step technique, although PTA may be a facile choice as this approach includes a microwave digestion process with concentrated nitric acid. The approach developed here enables CNT detection in a broad range of polymer-based consumer and industrial products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...