mRMR-based wavelength selection for quantitative detection of Chinese yellow wine using NIRS
Abstract
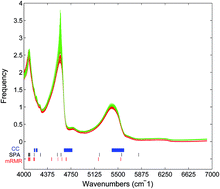
Wavelength selection plays an important role in near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy analysis. This paper introduces the minimal-redundancy-maximal-relevance (mRMR) algorithm into NIR analysis for wavelength selection, by which relevance between the spectrum and the target component is maximized while redundancy among selected wavelengths is minimized. The wavelength selection method is applied to predict the concentration of ethanol in Chinese yellow wine. The prediction performance of the mRMR algorithm is compared with two other widely used wavelength selection methods (the correlation coefficient method and the successive projections algorithm). Meanwhile, the adaptability of mRMR is verified by combining it with the partial least squares regression model and support vector regression. A total of 30 wavelengths were selected as the optimal set. The correlation coefficient, root mean square errors of prediction and residual predictive deviation were employed to evaluate the model performance, and the three indices reached 0.9848, 0.8159 and 3.6875 by mRMR based support vector regression. The results indicate that the mRMR algorithm can be applied to NIR analysis as an effective wavelength selection tool and has a stable prediction performance no matter which kind of regression method is used.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...