Covalent affixation of histidine-tagged proteins tethered onto Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid sensors for enhanced surface plasmon resonance detection of small molecule drugs and kinetic studies of antibody/antigen interactions
Abstract
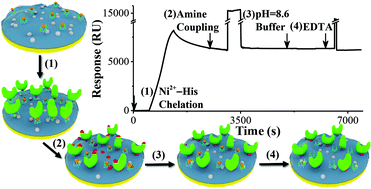
The Ni2+-histidine (His) chelation yields a more uniform and predicable orientation of immobilized protein molecules than an amine-coupling reaction in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analyses. However, the gradual dissociation of His-tagged proteins leads to a long and sloped baseline, which adversely affects kinetic studies. Furthermore, as shown in this work for the first time, the strong binding affinity between the histidine-rich Fc domain of immunoglobulin-type antibodies and Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) interferes with the kinetic studies of these antibodies and their His-tagged antigens. By performing an amine-coupling reaction immediately after the Ni2+-His chelation, essentially all of the Ni2+-tethered protein molecules can be covalently linked to the carboxyl groups on the underlying carboxymethylated dextran surface. The sequential injections of pH 8.6 phosphate-buffered saline provided additional time to ensure a higher amine coupling efficiency and reverted NHS esters on the protein molecules to carboxyl groups. The application of our method to antibody/antigen interactions is demonstrated with the kinetic analysis of His-tagged t-DARPP protein/anti-t-DARPP interactions. In a separate experiment, the highly efficient immobilization method resulted in a higher immobilization density of His-tagged human carbonic anhydrase (HCA) II, affording accurate kinetic measurements for the binding of 4-carboxybenzenesulfonamide. In addition, the higher HCA II density enhanced the SPR sensitivity, allowing 4-carboxybenzenesulfonamide to be determined with a remarkable detection limit (14 nM).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...