Sensor arrays made by self-organized nanoreceptors for detection and discrimination of carboxylate drugs†
Abstract
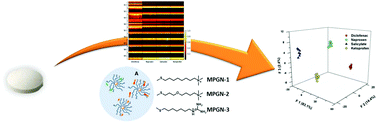
Nanoreceptors capable of recognizing amphiphilic organic carboxylates have been obtained by exploiting the self-organization properties of monolayer-protected gold nanoparticles. Affinity and selectivity for the target compounds can be modulated by modifying the chemical structure of the nanoparticle-coating molecules (cationic thiols). Such nanoreceptors have been used to develop sensor arrays in combination with different commercially available fluorescent dyes. The combined systems were tested for the detection and discrimination of four kinds of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The discriminatory capability of the sensing systems has been evaluated through pattern recognition methods, principle component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). The results showed that the systems here reported are able to identify the four kinds of NSAIDs with 100% accuracy in a quantitative way. The sensing system is capable of detecting the target drugs at micromolar concentration, discriminating both analyte identity and amount. In addition, the proposed sensor array is able to detect the four kinds of NSAIDs in a commercial tablet or in artificial urine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...