A triazine-based conjugated microporous polymer composite for magnetic solid phase extraction of 5-nitroimidazoles coupled with UPLC-MS/MS for quantification†
Abstract
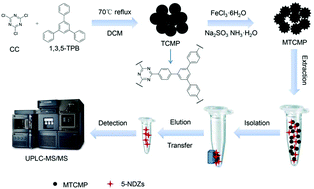
An attractive triazine-based conjugated microporous polymer (TCMP) was fabricated via the Friedel–Crafts reaction and magnetized by a simple reduction co-precipitation method for the first time. The morphology and textural properties of the as-synthesized materials were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, N2 adsorption measurements, elemental analysis, and magnetic measurements. The resulting magnetic triazine-based conjugated microporous polymer (MTCMP) was introduced as an efficient adsorbent for vortex-assisted magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) for the determination of trace 5-nitroimidazoles (5-NDZs) in environmental water samples. The TCMP has abundant delocalized π-electrons and N-containing triazine that can generate π-interactions, intermolecular hydrogen bonds, and electrostatic interactions with polar 5-NDZs. Extraction parameters affecting the recovery efficiency of five 5-NDZs (metronidazole, ronidazole, secnidazole, tinidazole, and ornidazole), including the amount of the adsorbent, the pH value of the sample, the salting-out effect, the adsorption and elution time, and types and volume of the elution solvents, were investigated. Under the optimal conditions, a wide linear range, acceptable recoveries (ranging from 82.62% to 110.9% with the relative standard deviation lower than 9.58%), and good reproducibility (relative standard deviations less than 8.81% for intra-day and inter-day precision) were obtained. The limits of detection for the five analytes were between 0.012 and 0.035 ng mL−1. The established method is rapid, has high sensitivity and accuracy, and has been successfully applied to the detection of 5-NDZs in real environmental water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...