In vivo measurement of the dynamics of norepinephrine in an olfactory bulb following ischemia-induced olfactory dysfunction and its responses to dexamethasone treatment
Abstract
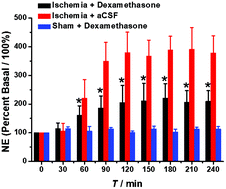
Information on the dynamics of molecules following olfactory dysfunction remains essential for understanding the molecular events involved in the pathological process of olfactory dysfunction. This study for the first time demonstrates a method based on the combination of in vivo microdialysis with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and electrochemical detection (ECD) for the measurement of the dynamics of norepinephrine (NE) in the olfactory bulbs of Sprague-Dawley rats following olfactory dysfunction induced by brain ischemia and its responses toward dexamethasone treatment. The method possesses a high spatial resolution and benefits from in vivo microdialysis and high selectivity and is thus capable of measuring NE in the olfactory bulb of rats. With this method, the basal level of NE in the olfactory bulb was evaluated to be ca. 235 ± 25 nM (n = 6). This level was found to increase by 260 ± 90% at a time point of 240 min after brain ischemia with bilateral ligation of both common carotid arteries. The increase was found to be suppressed upon the treatment of the animals with 0.2% dexamethasone in the olfactory bulb. These results suggest that NE is involved in the pathological process of ischemia-induced olfactory dysfunction and this information is useful to further understand the molecular events involved in olfactory dysfunction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...