A novel “signal-on” photoelectrochemical sensor for ultrasensitive detection of alkaline phosphatase activity based on a TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction†
Abstract
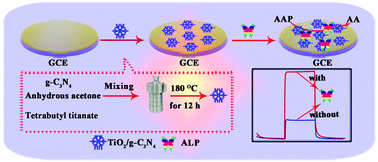
The use of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) as a biomarker in some diseases including hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, osteoblastic bone cancer, and osteomalacia is important in clinical diagnosis. Furthermore, ALP activity detection is an essential hot topic in environmental monitoring, biomedical research, and other research fields. In this study, a novel “signal-on” photoelectrochemical (PEC) biosensor based on the ALP-catalyzed phosphorylation reaction was designed to sensitively detect ALP activity. In this design, ascorbic acid—an electron donor—was catalytically produced by ALP from L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate trisodium salt in situ, which results in an increased photocurrent response signal. For immobilizing the ALP on the electrode surface, poly diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride was used for the conjugation of ALP, and titanium dioxide (TiO2)—a photoactive material—and graphite-like carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanocomposites were prepared and characterized. TiO2 attached on g-C3N4 plays an important role for the biosensing purpose due to their good biocompatibility and chemical/thermal stability, while g-C3N4 provides the PEC response signal. Furthermore, the prepared TiO2/g-C3N4 nanocomposites can effectively suppress electron–hole recombinations, improve the excitation conversion efficiency, and make the best use of solar energy. The PEC biosensor for ALP activity detection displays a detection limit of 0.03 U L−1 (S/N = 3), which offers a new route for the ALP activity assay in human serum samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...