In vitro FTIR microspectroscopy analysis of primary oral squamous carcinoma cells treated with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil: a new spectroscopic approach for studying the drug–cell interaction
Abstract
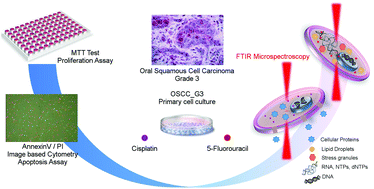
In the present study, human primary oral squamous carcinoma cells treated with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil were analyzed, for the first time, by in vitro FTIR Microspectroscopy (FTIRM), to improve the knowledge on the biochemical pathways activated by these two chemotherapy drugs. To date, most of the studies regarding FTIRM cellular analysis have been executed on fixed cells from immortalized cell lines. FTIRM analysis performed on primary tumor cells under controlled hydrated conditions provides more reliable information on the biochemical processes occurring in in vivo tumor cells. This spectroscopic analysis allows to get on the same sample and at the same time an overview of the composition and structure of the most remarkable cellular components. In vitro FTIRM analysis of primary oral squamous carcinoma cells evidenced a time-dependent drug-specific cellular response, also including apoptosis triggering. Furthermore, the univariate and multivariate analyses of IR data evidenced meaningful spectroscopic differences ascribable to alterations affecting cellular proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. These findings suggest for the two drugs different pathways and extents of cellular damage, not provided by conventional cell-based assays (MTT assay and image-based cytometry).
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...