Label-free and sensitive detection of Ochratoxin A based on dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles and exonuclease-catalyzed target recycling amplification
Abstract
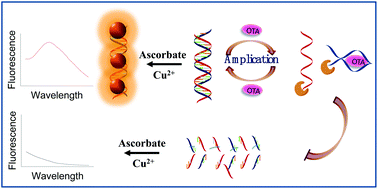
Ochratoxin A (OTA) is one of the most toxic mycotoxins and exists in various food commodities. Herein, a sensitive fluorescence method was developed for OTA detection which combines the advantages of label-free dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles (CuNPs), high selectivity of OTA aptamer and high efficiency of exonuclease-catalyzed target recycling amplification. OTA aptamer was hybridized with its complementary DNA (cDNA), and the obtained dsDNA acted as the template for fluorescent CuNPs. In the presence of its target (OTA), the aptamer prefers to form an OTA–aptamer complex in lieu of an aptamer–DNA duplex, which results in the dissociation of the aptamer–DNA duplex. The released cDNA and aptamer could be digested into mononucleotides by the RecJf exonuclease (single-stranded DNA specific exonuclease), and the target was liberated and could participate in the next reaction cycle. The above process resulted in the degradation of a large amount of template dsDNA, which prevented the synthesis of CuNPs, thus resulting in low fluorescence of the system. Based on this strategy, a label-free and sensitive detection of OTA was developed with a low detection limit of 5 ng mL−1 (S/N = 3). Our strategy was further validated and evaluated successfully by assaying OTA in real samples. The proposed assay has great potential as an OTA quantification method for use in the food safety field.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...