Highly sensitive detection of hesperidin using AuNPs/rGO modified glassy carbon electrode†
Abstract
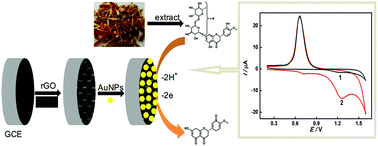
The highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor of hesperidin based on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) is reported. The AuNPs and rGO were uniformly introduced on the surface of the GCE via electrodeposition without any reducing agents and have been characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), FT-IR, and electrochemical methods. The AuNPs/rGO not only promoted the accumulation of hesperidin onto the GCE surface for quantitative analysis but also accelerated the electron transfer between hesperidin and the electrode substrates. Under the optimal conditions, hesperidin was determined quantitatively at the AuNPs/rGO/GCE using amperometric i–t curve. The results showed that the current obtained on detection of hesperidin exhibited a linear correlation with its concentration in the range of 5.0 × 10−8 mol L−1–8.0 × 10−6 mol L−1 with a detection limit of 8.2 × 10−9 mol L−1 (S/N = 3). In addition, good specificity, repeatability, reproducibility, and long-term storage stability were achieved for the modified electrode, which could be used for the detection of hesperidin in the traditional Chinese medicine, Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...