AS1411-decorated niosomes as effective nanocarriers for Ru(iii)-based drugs in anticancer strategies†
Abstract
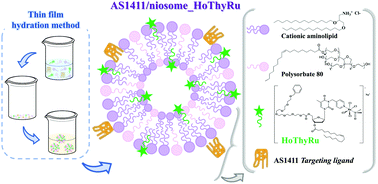
Niosomes are self-assembled vesicles made up of single chain non-ionic surfactants combined with appropriate amounts of cholesterol or other lipids, exploited as carriers for hydrophilic or lipophilic drugs. Compared to liposomes, niosomes are typically more stable, less expensive and, being generally obtained from synthetic surfactants, more easily derivatizable, providing vesicular structures with a higher versatility and chemical diversity. Herein, we investigated the physico-chemical and biological properties of niosomes loaded with two active ingredients, i.e. the nucleolipidic Ru(III)-complex HoThyRu, selected as an anticancer agent, and the nucleolin-targeting AS1411 aptamer, allowing selective recognition of cancer cells. The morphology, average size, zeta potential, electrophoretic mobility, and stability over time of the functionalized niosomes were analyzed using different biophysical techniques. These formulations, tested on both cancer and normal cells, showed promising antiproliferative activity on HeLa cells, with a higher efficacy associated with the nanosystems containing both AS1411 and HoThyRu with respect to the controls. In all the tested cell lines, AS1411 proved to markedly enhance the bioactivity of the Ru(III)-containing niosomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...