Interaction of SrO-terminated SrTiO3 surface with oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water†
Abstract
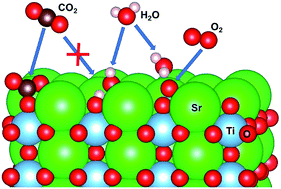
The interaction of SrO terminated SrTiO3 surface with molecular carbon dioxide and water has been investigated using first-principle theoretical methods and surface analysis techniques. We have studied the formation of a surface SrCO3 layer and various possible products of H2O interaction with the SrO surface, such as, surface chemisorbed water and the formation of a surface hydroxide layer. The co-adsorption of CO2 and H2O was explained both theoretically and experimentally showing that its products follow a complex temperature dependence and as a result, the surface composition may vary between carbonate and surface chemisorbed water. Our theoretical simulations have shown that the presence of water molecules in the gas phase might assist the molecular oxygen/lattice oxygen exchange reaction by stabilization of the surface oxo species in the transition state with a hydrogen bond mechanism. As a result, the activation barrier for molecular oxygen dissociation is decreased leading to an increase in the surface exchange rate constant. Our study demonstrates that the SrO terminated SrTiO3 surface is not static but instead, dynamically responds to external factors such as gas composition, humidity, and temperature. As a result, the surface phases can show different trends for the surface exchange reaction with molecular oxygen by either an increase or decrease in the exchange rate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...