CO2 and water activation on ceria nanocluster modified TiO2 rutile (110)†
Abstract
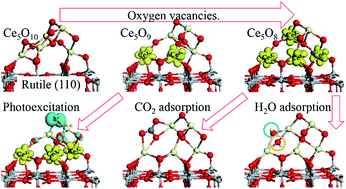
Surface modification of TiO2 with metal oxide nanoclusters is a strategy for the development of new photocatalyst materials. We have studied modification of TiO2 rutile (110) with ceria nanoclusters using density functional theory corrected for on-site Coulomb interactions (DFT+U). We focus on the impact of surface modification on key properties governing the performance of photocatalysts, including light absorption, photoexcited charge carrier separation, reducibility and surface reactivity. Our results show that adsorption of the CeO2 nanoclusters, with compositions Ce5O10 and Ce6O12, is favourable at the rutile (110) surface and that the nanocluster–surface composites favour non-stoichiometry in the adsorbed ceria so that reduced Ce ions will be present in the ground state. The presence of reduced Ce ions and low coordinated O sites in the nanocluster lead to the emergence of energy states in the energy gap of the TiO2 host, which potentially enhance the visible light response. We show, through an examination of oxygen vacancy formation, that the composite systems are reducible with moderate energy costs. Photoexcited electrons and holes localize on Ce and O sites of the supported nanoclusters. The interaction of CO2 and H2O is favourable at multiple sites of the reduced CeOx–TiO2 composite surfaces. CO2 adsorbs and activates, while H2O spontaneously dissociates at oxygen vacancy sites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...