Bilayers of Janus and homogeneous particle mixtures trapped at an air/water interface†
Abstract
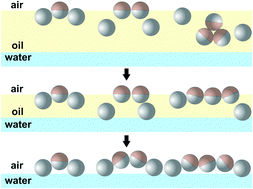
We study mixtures of amphiphilic Janus and homogeneous hydrophobic particles trapped at an air/water interface. In contrast to an expected monolayer formation, bilayers of colloidal particles are produced. Despite their strong interfacial adsorption, Janus particles form the upper layer. They are not placed on top of the other particles but rather shifted about one-third of the particle diameter. To understand the mechanism of bilayer formation, particle behaviour at the surface and in the bulk of the spreading solvent is considered. The vertical shift and the bilayer formation are assisted by the momentous formation of two interfaces during spreading.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...