Effect of geometrical parameters on rebound of impacting droplets on leaky superhydrophobic meshes†
Abstract
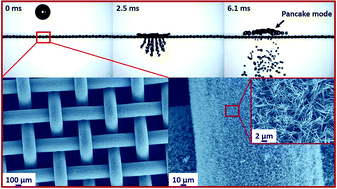
When a droplet impacts a superhydrophobic sieve, a part of the droplet penetrates through it when the dynamic pressure (ρU2) of the impinging droplet exceeds the breakthrough pressure (γΓ/A). At higher impact velocities, the ejected-jet breaks and separates from the main droplet. The remaining part of the droplet bounces off the surface showing different modes (normal bouncing as a vertically elongated drop or pancake bouncing). In this work, we have studied the effect of different geometrical parameters of superhydrophobic copper meshes on different modes of droplet rebound. We observe three different effects in our study. Firstly, we observe pancake like bouncing, which is attributed to the capillary energy of the rebounding interface formed after the breaking of the ejected-jet. Secondly, we observe leakage of the droplet volume and kinetic energy due to the breaking of the ejected-jet, which leads to reduction in the contact times. Finally, we observe that for flexible meshes, the transition to pancake type bouncing is induced at lower Weber numbers. Flexibility also leads to a reduction in the volume loss from the ejected-jet. This study will be helpful in the design of superhydrophobic meshes for use under impact scenarios.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...