Multiphasic aqueous hydroformylation of 1-alkenes with micelle-like polymer particles as phase transfer agents†
Abstract
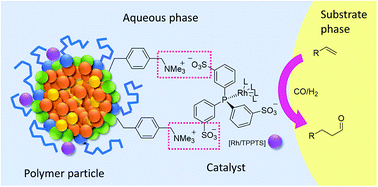
Micelle-like polymer particles have been applied in aqueous multiphasic hydroformylation reactions of long chain alkenes. These colloids act as phase transfer agents for the nonpolar substrates and as carriers for the catalyst bearing sulfonated ligands by electrostatic attraction. The catalyst performance and the phase separation were optimized with special focus on the conversion, selectivity and catalyst recovery, as those are key points in multiphasic systems to achieve a feasible industrial process. The effect on the catalyst performance of the number of sulfonate groups and electron withdrawing trifluoromethyl groups in the ligand has been studied. The approach was successfully demonstrated for 1-alkenes from 1-hexene to 1-dodecene. For 1-octene, a TOF of more than 3000 h−1 could be achieved at a substrate to catalyst ratio of 80 000, while keeping the rhodium and phosphorous leaching below 1 ppm. In repetitive batch experiments the catalyst was recycled four times, yielding an accumulated TON of more than 100 000 for 1-octene.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...