Biochar production and applications in soil fertility and carbon sequestration – a sustainable solution to crop-residue burning in India†
Abstract
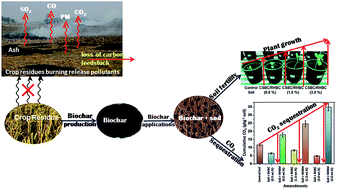
A sustainable solution to biomass burning by converting agricultural residues into biochar was provided. Biochar application was investigated to improve soil fertility, sequester carbon, and increase crop production. Rice husk (RHBC) and corn stover (CSBC) biochars were obtained by slow pyrolysis at 650° and 550 °C, respectively. RHBC and CSBC were characterized (SEM, SEM-EDX, TEM, FTIR, XRD, elemental analyses, and SBET). Unpyrolyzed husks and stover were also used for soil amendments and compared to biochars in different proportions under a controlled incubation environment over 107 days. Fertilizers were not applied. An increase in water holding capacity, total organic carbon, cation exchange capacity, and a decrease in soil CO2 emission were observed after biochar application to soil versus the application of the parent husks or stover. These biochars improved soil fertility and enhanced eggplant crop growth (height, leaf number, fresh and dry weight). In addition, carbon mitigation was achieved because the biochar remained stable in the soil achieving longer term carbon sequestration. Both chars can be used for carbon sequestration and soil amendments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...