A peptide inhibitor of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity against EGFR/folate receptor-α double positive cells†
Abstract
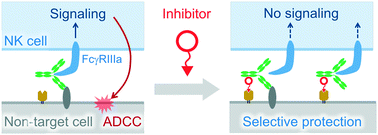
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is caused by natural killer (NK) cells upon recognition of antigen-bound IgG via FcγRIIIa. This mechanism is crucial for cytolysis of pathogen-infected cells and monoclonal antibody (mAb)-mediated elimination of cancer cells. However, there is concern that mAb-based cancer therapy induces ADCC against non-target cells expressing antigens. To date, no strategy has been reported to enhance the selectivity of ADCC to protect non-target cells expressing antigens. Here, we introduce a model inhibitor which specifically blocks ADCC of anti-EGFR mAbs towards EGFR/folate receptor α (FRα) double positive cells. This inhibitor recruits mAbs on the FRα of the cell surface independent of Fab antigen recognition. The resulting ternary and/or quaternary complexes formed on the cell surface suppress signal transduction of FcγRIIIa in NK cells, consequently leading to more specific ADCC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...