Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY04 exhibits a strain-specific property of lowering TMAO via the modulation of gut microbiota in mice†
Abstract
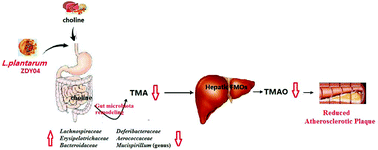
Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), which is oxidized from trimethylamine (TMA) by hepatic flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMOs), promotes the development of atherosclerosis and is a new target for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease from the perspective of intestinal flora. TMA is transformed by intestinal flora from TMA-containing nutrients, such as choline. Some small molecular agents lower serum TMAO and/or cecal TMA levels. However, probiotics that can effectively reduce serum TMAO levels are currently lacking. In this work, five potentially probiotic strains were administered to mice supplemented with 1.3% choline. Only Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY04 significantly reduced serum TMAO and cecal TMA levels by modulating the relative abundance of the families Lachnospiraceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Bacteroidaceae and the genus Mucispirillum in mice and not by influencing the expression levels of hepatic FMO3 and metabolizing choline, TMA, and TMAO. In addition, L. plantarum ZDY04 can significantly inhibit the development of TMAO-induced atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− 1.3% choline-fed mice as compared with the untreated PBS group. In conclusion, the use of L. plantarum ZDY04 may be an alternative approach to reduce serum TMAO levels and TMAO-induced atherosclerosis in mice.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...