Rooibos tea extracts inhibit osteoclast formation and activity through the attenuation of NF-κB activity in RAW264.7 murine macrophages
Abstract
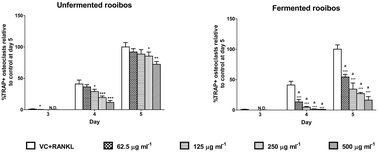
Rooibos tea is a naturally sweet and aromatic tea that is native to the Western Cape province of South Africa. Rooibos is usually fermented to produce the traditional reddish brown colour and has been found to have numerous health benefits. These include beneficial effects on osteoblasts; however, its effects on osteoclast formation and activity are unknown. Osteoclasts are large, multinucleated cells responsible for bone resorption. Binding of RANKL to its receptor on osteoclast precursors triggers the NF-κB signalling pathway leading to the formation of osteoclasts. Certain bone destructive diseases, such as osteoporosis, are characterised by overactive osteoclasts. The inhibition of osteoclasts may offer a potential mode to prevent these diseases. The polyphenol contents of both fermented and unfermented tea extracts were similar although the radical scavenging activity of fermented rooibos tea was lower. Both tea extracts were not cytotoxic and inhibited osteoclast formation. Fermented rooibos tea extract caused a greater reduction in osteoclast resorption and the associated gene expression when compared with unfermented rooibos tea. Both tea extracts were shown to attenuate NF-κB activity. Fermented rooibos was found to have a more potent inhibitory effect on osteoclasts than unfermented rooibos extract and therefore may have a beneficial effect on bone health.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...