In silico estimation of chemical aquatic toxicity on crustaceans using chemical category methods†
Abstract
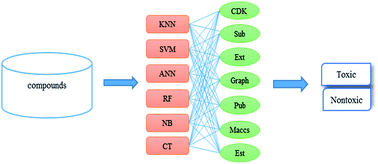
With industrial development and eventual commercial use, environmental chemicals through accidental spills and effluents appear more frequently in aquatic ecosystems and may produce an enormous effect on water, soil, wildlife and human health. Therefore, aquatic toxicity becomes an increasingly important endpoint in the evaluation of the environmental impact of chemicals. In this study, based on ECOTOX database, a large data set containing 824 diverse compounds with experimental 48 h EC50 values on crustaceans was compiled. A series of in silico models were then developed using six machine learning methods combined with seven types of molecular fingerprints. Performance of these models was measured by an external validation set, involving 246 molecules. The best model proposed is MACCS fingerprint and SVM algorithm with high accuracy of 0.87 for external validation set. Additionally, we proposed five structural alerts identified by information gain and substructure frequency analysis for mechanistic interpretation. The models and structural alerts can provide critical information and useful tools for a priori evaluation of chemical aquatic toxicity in environmental hazard assessment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...