Tin(ii) oxide carbodiimide and its relationship to SnO†
Abstract
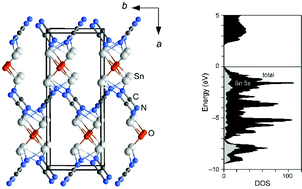
The compound Sn2O(CN2) was obtained as a brick-red crystalline powder from a solid-state reaction of equimolar amounts of SnCl2, SnO and Li2(CN2). Thermal analysis of the reaction indicates the formation of two intermediate compounds until Sn2O(CN2) is formed at 400 °C. The crystal structure of Sn2O(CN2) was determined in the space group Pccn (a = 13.3949(7) Å, b = 5.2954(3) Å, c = 5.5369(2) Å, Z = 4) from single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. The structure contains a Sn2+ ion with a 5s2 lone pair, situated in a fourfold, mixed O-/N-coordination environment. The crystal structure of Sn2O(CN2) is analyzed and discussed in relation to that of SnO, namely by electronic-structure calculations and a COHP bonding analysis of Sn2O(CN2).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...