One-step green synthesis of composition-tunable Pt–Cu alloy nanowire networks with high catalytic activity for 4-nitrophenol reduction†
Abstract
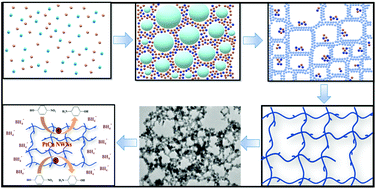
Controlling the structure, morphology, and composition of noble metals is of great significance to improve the catalytic activity and stability of catalysts. Herein, we have successfully synthesized self-interconnecting Pt–Cu alloy nanowire networks (NWNs) with controllable compositions via the co-reduction of the metal precursors potassium chloroplatinate (K2PtCl6) and CuCl2 with sodium borohydride (NaBH4). Owing to the hydrogen bubbles formed by NaBH4 hydrolysis and oxidation as a dynamic template, the facile strategy was carried out without any organic solvent, capping agent, polymer, or special experimental device, ensuring that the surfaces of NWNs were definitely “clean”. The performance of the as-prepared Pt–Cu alloy NWNs for the reduction of 4-NP was dramatically improved compared with that of pure Pt NWNs and the commercial Pt/C catalyst. Particularly, the PtCu NWNs with a Pt/Cu atomic ratio of 1 : 1 exhibited excellent catalytic activity and reusability for the reduction of toxic 4-NP. The reaction rate constant and activity factor of the PtCu NWNs reached 1.339 × 10−2 s−1 and 66.95 s−1 g−1, respectively, which were dramatically better than those of pure Pt NWNs (11.5-fold) and commercial Pt/C (13-fold). The superior catalytic activity and reusability can mainly be attributed to the clean surface, the synergistic effect of Cu and Pt atoms and the self-interconnecting nanowire network structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...