Combining catalysis and computational fluid dynamics towards improved process design for ethanol dehydration†
Abstract
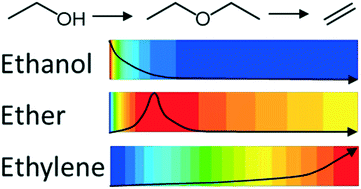
Through a combined computational fluid dynamics, characterization and catalysis study we have developed, for the first time, a working model of the ethanol dehydration process within a catalytic pelletized fixed bed reactor. The model, constructed from experimental kinetic data on the dehydration of ethanol to ethylene, with the industrial MTO catalyst SAPO-34, provides unique insights on reaction rate, product selectivity and local temperature fluctuations that are pivotal to reactor design towards optimized catalytic processes, and highly relevant for the optimization of industrial chemical processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...