Single-compartment hydrogen peroxide fuel cells with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) cathodes
Abstract
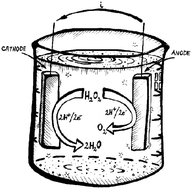
Single-compartment hydrogen peroxide fuel cells have recently emerged as a promising energy conversion platform since H2O2 is a high energy-density liquid that functions as both fuel and oxidizer. Finding suitable electrocatalysts is challenging since most metallic electrodes also catalyze the disproportionation reaction of H2O2 into H2O and O2, representing a significant loss mechanism in peroxide fuel cells. Herein we demonstrate that the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene), PEDOT, is a versatile electrocatalyst for peroxide fuel cells without generating losses due to disproportionation. We find that PEDOT is a cathodic catalyst for reduction of peroxide to water, performing at a level on par with the best reported inorganic catalysts. Using PEDOT as the cathode and nickel as the anode material, open circuit potentials in the range of 0.5–0.6 V are possible, with power densities of 0.20–0.30 mW cm−2. We provide evidence to understand mechanistically how PEDOT functions as a catalyst for hydrogen peroxide reduction to water. The result of our efforts is a scalable hydrogen peroxide fuel cell cathode, which serves to demonstrate also the capabilities of organic semiconducting materials as electrocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...