Protective effects of coenzyme Q10 and resveratrol on oxidative stress induced by various dioxins on transheterozigot larvae of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
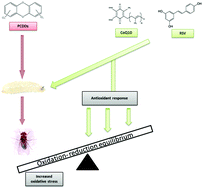
Dioxin and dioxin-like compounds are known as a class of highly toxic and persistent environmental contaminants threatening human and animal health. In the present study, the protective effects of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and Resveratrol (RSV) against 2,3,7,8-TCDD, 1,2,3,7,8-PeCDD, 1,2,3,7,8,9-HxCDD, and 1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9-OCDD induced acute toxicity and measurement of oxidative stress were studied. Lethal doses of these chemicals were determined. Transheterozigot larvae of Drosophila melanogaster were treated using either dioxins (10 × 10−7 μg mL−1) or dioxins + CoQ10 (10 × 10−7 μg mL−1 + 150 μg mL−1) and dioxins + RSV (10 × 10−7 μg mL−1 + 100 μM). After dioxin treatment, antioxidant combination therapy with dioxins and CoQ10 or dioxins and RSV resulted in indicators of acute toxicity including a decrease in total oxidant status as compared to dioxins alone (p < 0.05). The combination treatment also produced a significant increase in total antioxidant status as compared to dioxins only (p < 0.05). Results indicate a potential role of dioxins for oxidative stress with acute toxicity and the protective performance of CoQ10 and RSV in the overall toxicity of dioxins including measuring oxidative stress.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...