The muscarinic effect of anhydroecgonine methyl ester, a crack cocaine pyrolysis product, impairs melatonin synthesis in the rat pineal gland
Abstract
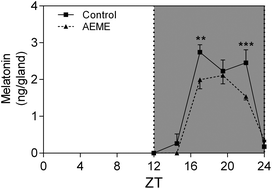
Anhydroecgonine methyl ester (AEME), also called methylecgonidine, is a pyrolysis product of crack cocaine that is neurotoxic and potentiates cocaine-induced sensitization. The sensitization induced by drugs of abuse can be influenced by melatonin, a neuroprotective pineal hormone. In the same way, drugs of abuse like alcohol and methamphetamine can modify melatonin synthesis. The aim of the present work was to investigate the AEME effects on melatonin synthesis in the rat pineal gland. Neurotransmitter systems involved in its effects, antioxidant enzyme activities and the melatonin protective role in AEME-induced toxicity were also evaluated. The animals were injected with AEME i.p. (1.12 mg per kg of body weight per day) or vehicle for 10 consecutive days and the nocturnal pineal melatonin synthesis profile and SOD, GPx and GR activities in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus were assessed. Cultured pineal glands were incubated with AEME for 30 min or 48 h before norepinephrine stimulation and melatonin synthesis, arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase activity, cAMP and [Ca2+]i were determined. The involvement of cholinergic and glutamatergic systems was analyzed using different antagonists. The protective role of melatonin in AEME toxicity on hippocampal neurons was evaluated by a viability assay. AEME impaired melatonin synthesis both in vivo and in vitro and this effect seems to be mediated by muscarinic receptors and [Ca2+]i elevation. AEME reduced neuronal viability and melatonin was able to protected hippocampal neurons against AEME toxicity. The melatonin synthesis impairment observed could lead to the worsening of the direct AEME neurotoxicity and to the exacerbation of the crack cocaine addiction and sensitization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...