Investigating the impact of conjugation pathway on the physical and electronic properties of benzobisoxazole-containing polymers†
Abstract
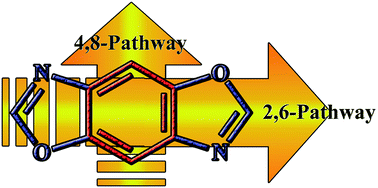
Six new isomeric benzobisoxazole (BBO)-containing polymers have been synthesized and characterized to elucidate structure–property relationships in the materials. In one series, the polymer backbone is connected at the oxazole rings of the BBO, while in the other series, the backbone passes directly through the central benzene ring, leaving the oxazole rings perpendicular to the polymer backbone. The impact of BBO connectivity on the optical and electronic properties of the materials was evaluated spectroscopically. Additionally, the polymers’ performance as fluorescent guest emitters in host–guest polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs) was also examined. It is found that the BBO orientation in which the oxazole rings are perpendicular to the backbone reduces the optical band gap and significantly increases the efficiency of resonance energy transfer between the PLED host material and the BBO-containing light-emitting polymer guest, resulting in improved external quantum efficiencies of the PLEDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...