Triphenylethylenyl-based donor–acceptor–donor molecules: studies on structural and optical properties and AIE properties for cyanide detection†
Abstract
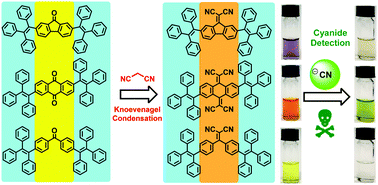
Six novel molecules with donor–acceptor–donor (D–A–D) configurations were synthesized with a middle acceptor flanked by two electron-rich triphenylthylenyl moieties. The first set of three molecules (TPE-FLN, TPE-AQN and TPE-BZQ) consists of fluorenone, anthraquinone and benzophenone as acceptors, respectively, which then underwent Knoevenagel condensation with malononitrile to give the second set of 1,1-dicyanomethylidene-containing molecules CS1, CS2 and CS3. Compounds CS1, CS2 and CS3 were found to be selective to nucleophilic attack by cyanide ion and hence their potential as optical cyanide sensors was investigated. It was found that the main cyanated products of CS1 and CS3 were aggregation-induced emission (AIE) active, and they were successfully isolated and fully characterized. Finally, paper probes were fabricated from the three compounds, of which the CS1-coated paper probe gave a remarkable turn-on of fluorescence in the presence of cyanide, revealing potential for use as a cyanide sensor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...