Effect of Cu/In ratio and shell thickness on the photo-stability of CuInS2/ZnS nanocrystals†
Abstract
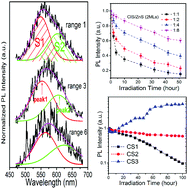
CuInS2 core nanocrystals (NCs) with different Cu/In ratios are synthesized, and a rapid synthesis method is used to overcoat ZnS shells onto them. A time-resolved photoluminescence study revealed that a broad PL peak consists of the contribution from two kinds of donor–acceptor pairs (DAPs), and as indicated by photo-stability measurements, higher energy DAPs are sensitive to irradiation, resulting in the photo-instability of CuInS2 NCs. The intensity ratio between high-energy DAPs and low-energy ones is decreased with the decrease of the Cu/In ratio, and it is suggested that the high energy DAPs are near the core/shell interfaces, and the low energy ones are inside the cores. The shell's overcoating, which would keep the higher energy DAPs away from the surroundings, could improve the photo-stability of the NCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...