The role of Ln3+ (Ln = Eu, Yb) in persistent red luminescence in MgGeO3:Mn2+†
Abstract
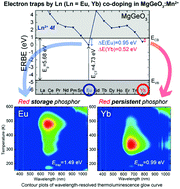
In this paper, Mn2+ and Ln3+ (Ln = Eu, Yb) co-doped MgGeO3 phosphors were prepared using a solid state reaction technique, and their optical properties were investigated. Mn2+-doped samples exhibit persistent luminescence in the red region, peaking at 677 nm, because of the 4T1 → 6A1 transition of the Mn2+ ions under ultraviolet (UV) excitation. Based on the charge transfer (CT) transition of Eu3+ and the band-gap energy, energy level diagrams with divalent lanthanide ground states relative to the conduction and valence band edges were constructed. ΔE(Ln), (Ln = Eu, Yb), which represents the energy gaps between the divalent lanthanide ground states and the bottom of the conduction band, were found to be 0.95 and 0.52 eV, respectively. Compared to a Mn2+ singly-doped sample, the thermoluminescence (TL) glow curves of the Mn2+–Eu3+ co-doped sample and the Mn2+–Yb3+ co-doped sample showed an additional TL glow peak at approximately 502 and 332 K with trap depths (Etrap) of 1.49 and 0.99 eV, respectively. The correspondence of Etrap with ΔE(Ln) suggests that Eu3+ and Yb3+ themselves work as electron traps in the MgGeO3:Mn2+ phosphors. We have also demonstrated that the Mn2+–Eu3+ co-doped material could be a good probe with photo-stimulated functions for long-term in vivo imaging owing to its deeper trap depth.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...