Exploring the effects of interfacial carrier transport layers on device performance and optoelectronic properties of planar perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
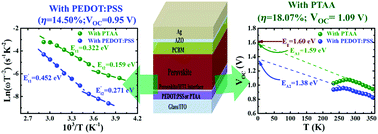
We investigated the effects of carrier transport layer on performance of perovskite device and limitation factors by analysing the optoelectronic properties. The device efficiency was enhanced from ∼14.5% to ∼18.1% by replacing hole transport layer (HTL) PEDOT:PSS with PTAA, governed by increase in open circuit voltage and short circuit current. We found that PTAA device leads to the improvement in interface layer quality, efficient carrier transport and mitigation of bulk defect activities. The analysis of temperature and intensity dependent current–voltage characteristics suggests that PEDOT:PSS device is limited by interface and trap assisted recombination. The capacitance spectroscopy and electroluminescence revealed soothing of recombination activities as a consequence of better interface quality and shallower defect level for PTAA device. Our results consolidate that the perovskite film and interface quality and recombination activities in device are dominantly influenced by HTLs which pave a way for further enhancement in efficiency coupled with excellent interfacial carrier transport layer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...