Effective band gap tuning by foreign metal doping in hybrid tin iodide perovskites
Abstract
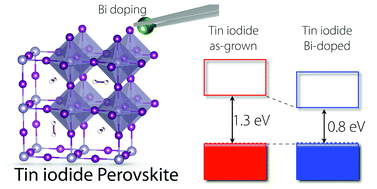
Herein, we introduce a novel effective band tuning method in hybrid tin iodide perovskites using a different group element. With this method, band gap reduction down to 0.8 eV is observed in tin (group 14) iodide-based hybrid perovskites as a result of bismuth (group 15) doping. In this solution-processable material, the band gap is continuously controllable in the range from 1.3 to 0.8 eV even when the doping level was less than 10%. The effect of “foreign metal” doping on the band gap is larger than that of the mixed crystal with the same group elements. Bismuth doping reduces the conductivity of the materials depending on the doping levels though their behavior is still clearly metallic. From the results of the electronic structure and electronic properties of this material, it is clear that bismuth doping causes the narrowing of the band gap without changing the energy and DOS at the top of the valence band, and without increasing the number of carriers. The band tuning method will be useful for the design of solar cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...