Rapid laser-induced photochemical conversion of sol–gel precursors to In2O3 layers and their application in thin-film transistors†
Abstract
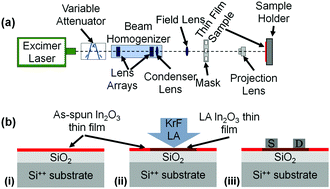
We report the development of indium oxide (In2O3) transistors via a single step laser-induced photochemical conversion process of a sol–gel metal oxide precursor. Through careful optimization of the laser annealing conditions we demonstrated successful conversion of the precursor to In2O3 and its subsequent implementation in n-channel transistors with electron mobility up to 13 cm2 V−1 s−1. Importantly, the process does not require thermal annealing making it compatible with temperature sensitive materials such as plastic. On the other hand, the spatial conversion/densification of the sol–gel layer eliminates additional process steps associated with semiconductor patterning and hence significantly reduces fabrication complexity and cost. Our work demonstrates unambiguously that laser-induced photochemical conversion of sol–gel metal oxide precursors can be rapid and suitable for the manufacturing of large-area electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...