Chiral recognition of optically active CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles by CdSe/CdS quantum dots stabilised with chiral ligands†
Abstract
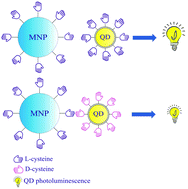
We report a new optical sensing approach based on the chiral recognition of optically active CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles by CdSe/CdS core/shell quantum dots stabilized with cysteine of different chiralities. In our work, chiral recognition of magnetic nanoparticles was demonstrated by specific quenching of chiral quantum dot photoluminescence with chiral magnetic nanoparticles. It was found that nanoparticles stabilized with complementary enantiomers interact with each other more effectively than those with identical enantiomeric ligands and therefore, quenching was much more pronounced for these nanoparticles. This chiral recognition can be explained by the specific chiral defects on the magnetic nanoparticle surface formed during the synthesis, which enable the enantioselective attachment of QD cysteine ligands to the magnetic nanoparticle surface. This new approach can be used in chemical and biomedical applications involving optical chiral sensing and detection of various enantiomeric species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...