Self-assembled RGD dehydropeptide hydrogels for drug delivery applications†
Abstract
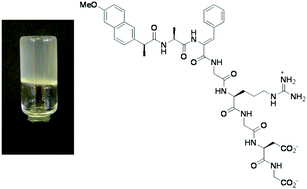
Peptide-based self-assembled hydrogels have triggered remarkable research interest in recent years owing to their biocompatibility and biomimetic properties and responsiveness, which warrant many technological and biomedical applications. Dehydrodipeptides N-capped with naproxen emerged from our research as effective hydrogelators endowed with resistance to proteolysis. Dehydrodipeptide-based hydrogels are promising nanocarriers for drug delivery applications. In this work, we demonstrate that dehydrodipetide Npx-L-Ala-Z-ΔPhe-OH can be deployed as a minimalist hydrogelator module for synthesizing a gelating construct Npx-L-Ala-Z-ΔPhe-G-R-G-D-G-OH bearing a GRGDG adhesion motif. The self-assembly of the peptide construct and the drug delivery properties of the hydrogel were studied in this work. The peptide construct showed no toxicity towards a fibroblast cell line expressing the αvβ3 integrin. Docking studies suggest that the hydrogelator block does not interfere with the recognition of the RGD motif by the integrin receptor. The self-assembly seems to be directed by intermolecular naphthalene π–π stacking interactions, with the peptide backbone assuming a random coil conformation both in solution and in the gel phase. TEM and STEM imaging revealed that the hydrogel is made of entangled bundles of long thin fibres (width circa 23 nm). The hydrogel exhibits viscoelastic properties, thermo-reversibility and recovery after mechanical fluidization. FRET studies showed that curcumin incorporated into the hydrogel interacts non-covalently with the hydrogel fibrils. Delivery of curcumin from the hydrogel into Nile red loaded model membranes (SUVs) was demonstrated by FRET. Naproxen N-capped dehydrodipeptides are efficacious minimalist hydrogelator modules for obtaining hydrogels functionalized with peptide ligands for cell receptors. These hydrogels are potential nanocarriers for drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...