Synthesis of water-soluble and highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters for Fe3+ sensing in living cells using fluorescence imaging†
Abstract
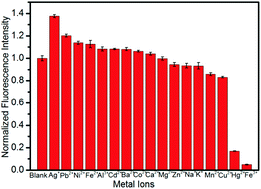
Gold nanoclusters are used as excellent scaffolds for the development of chemical and biological sensors due to their outstanding physical and chemical properties. In this study, a facile and green method has been employed for the preparation of highly fluorescent Au NCs by simply heating the gold precursor solution in the presence of a specially designed multidentate polymer ligand PTMP–PMAA. Herein, PTMP–PMAA functions as a reducing agent as well as a protecting agent. The Au NCs were characterized by fluorescence spectroscopy, ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering (DLS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF), and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and were found to exhibit yellow fluorescence (λem = 553 nm), a high quantum yield (22.6%), excellent stability and water-solubility. Based on aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching, the Au NCs@PTMP–PMAA fluorescent NCs were used for the detection of Fe3+ with an acceptable sensitivity having a detection limit of 3.0 μM and high selectivity. Moreover, Au NCs were also explored for the fluorescence imaging of Fe3+ in living H9c2 cardiac muscle cells presenting internalization with green fluorescence from the cells, suggesting their potential applicability as bioimaging agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...