The improvement of corrosion resistance, biocompatibility and osteogenesis of the novel porous Mg–Nd–Zn alloy†
Abstract
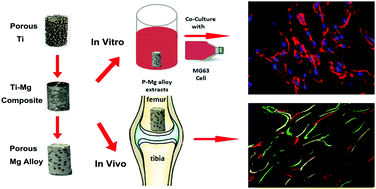
A magnesium scaffold is a promising biodegradable bone repair material. However, its poor corrosion resistance limits its clinical application. In this study, we improved the corrosion resistance, biocompatibility and osteointergration ability of magnesium by alloying it with neodymium (Nd) and zinc (Zn), then fabricated a novel open-porous Mg–Nd–Zn (P-MNZ) alloy using a titanium wire space holder (TWSH) method. An in vitro corrosion experiment showed that corrosion resistance was enhanced. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments were performed to evaluate the biocompatibility and osteointergration ability of P-MNZ. The cell viability, cytoskeleton staining, ALP activity and osteogenic related gene expression confirm that the P-MNZ scaffold exhibits better biocompatibility and osteoblast differentiation properties in vitro. As for the in vivo experiment, the analysis of micro-CT scanning, Van Gieson staining and sequential polychrome labelling demonstrated that P-MNZ stimulates new bone formation and enhances the corrosion resistance of the P-MNZ scaffold. The results indicate that the P-MNZ alloy is a promising biodegradable bone repair material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...