Multiple gold nanorods@hierarchically porous silica nanospheres for efficient multi-drug delivery and photothermal therapy†
Abstract
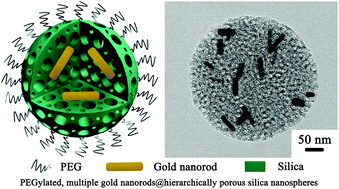
Gold-based nanocomposites have attracted intensive attention due to their unique optical properties and great potential in biomedical applications. Herein, we report a simple route for the synthesis of multiple gold nanorods encapsulated, hierarchically porous silica nanospheres (MGNRs@HPSNs) based on the cooperative self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymer polystyrene-b-poly (acrylic acid) (PS-b-PAA), cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB), gold nanorods and the organosilane of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) in an oil/water system. Multiple gold nanorods have been loaded successfully into the interior of the hierarchically porous silica nanospheres, which consist of large, interconnected pores of 13.2 nm throughout the whole sphere and small pores of 2.7 nm in the silica framework. Moreover, the loading amount (or number) of gold nanorods in the silica matrix can be tuned by simply changing the initial concentration of preformed gold nanorods. Due to the presence of the hierarchically porous structure, the PEGylated MGNRs@HPSNs display high loading capability for both small anti-tumor drugs (i.e., doxorubicin hydrochloride, 69.2 ± 7.2 mg g−1) and bio-macromolecules (i.e., bovine serum albumin, 248.1 ± 12.3 mg g−1). More importantly, MGNRs@HPSNs present better photothermal effect than that of hierarchically porous silica nanoparticles containing less (one or two) gold nanorods at the same Au concentration. It is thus demonstrated that MGNRs@HPSNs can not only act as promising drug/protein nanocarriers, but also can be used as photoabsorbers for photothermal tumor therapy under NIR laser irradiation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...