Nitrogen-doped porous carbons derived from isomeric metal azolate frameworks†
Abstract
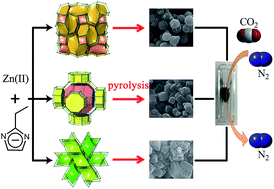
Pyrolysis treatments of three [Zn(eim)2] (Heim = 2-ethylimidazole) supramolecular isomers, namely MAF-5 (ANA, 38.6%), MAF-6 (RHO, 55.4%) and MAF-32 (qtz, 0%), possessing different network topologies and porosities, gave morphology-retaining, nitrogen-doped porous carbons denoted as CMAF-5, CMAF-6 and CMAF-32, respectively. Elemental analyses gave nitrogen contents of CMAF-32 (5.45%) > CMAF-5 (5.05%) > CMAF-6 (2.55%), indicating that larger pores are beneficial for the removal of nitrogen contents. Ar sorption measurements for CMAF-5/CMAF-6/CMAF-32 gave pore volumes and surface areas of 0.42/0.65/0.35 cm3 g−1 and 1027/1453/730 m2 g−1, respectively, which are higher than those of their precursors but showing the same trend. The pore sizes of CMAF-5/CMAF-6/CMAF-32 mainly distribute in the ultramicroporous region of 3.7 to 7.5 Å, but still follow CMAF-32 < CMAF-5 < CMAF-6, coincident with the porosities of their precursors. These carbons show remarkable CO2 sorption and CO2/N2 selectivities, consistent with their pore sizes and nitrogen contents. Notably, the IAST CO2/N2 (v/v = 15 : 85, 298 K and 1 bar) selectivities of CMAF-5 and CMAF-32 reach 180 and 262, respectively, which are the highest among all known porous carbon materials. Mixed-gas breakthrough experiments using a 15 : 85 CO2/N2 mixture gave a CO2/N2 selectivity of 234 for CMAF-32.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...