Recent advances in ternary two-dimensional materials: synthesis, properties and applications
Abstract
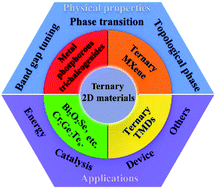
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have gained significant attention owing to their unique physical and chemical properties, which arise mainly from their high surface–bulk ratios and topological effects. Since the discovery of graphene in 2004, the family of 2D materials has expanded rapidly. Thus far, several single-element 2D materials (graphene, phosphorene, etc.) have been reported; the majority of them contain two (MoS2, WSe2, etc.) or more elements (Mo2CTx, CrPS4, Bi2Sr2CaCu2Ox, etc.). Of these, three-element 2D materials, also called ternary 2D materials, represent a rather attractive direction of recent years. Typical ternary 2D materials include metal phosphorous trichalcogenides (MPTs), ternary transition metal chalcogenides (TMDs), transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) and 2D ternary oxides. Ternary 2D systems result in multiple degrees of freedom to tailor their physical properties via stoichiometric variation. Moreover, they exhibit some properties not characteristic of binary 2D systems, such as band gap tuning. In this paper, we have reviewed the recent progress in various ternary 2D materials on the basis of their classification (MPTs, ternary 2D MXenes, ternary TMDs, BCN and other ternary 2D materials). The synthesis methods, structures, key properties (such as band gap tuning, phase transition and topological phase), and their applications, are summarized. In addition, the strategies to tackle challenges, as well as the outlooks of this field, are presented.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...