Ultra-high proton/vanadium selectivity of a modified sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) composite membrane for all vanadium redox flow batteries†
Abstract
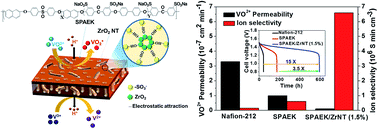
An ultra-high ion-selective membrane composed of an aromatic block copolymer sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) (SPAEK) and ZrO2 nanotubes (ZrNTs) is designed and fabricated via a solution-casting method. The composite membrane showed high proton conductivity and a reduced VO2+ crossover rate compared with a pristine SPAEK membrane. The SPAEK/ZrNT composite membrane exhibits a high proton conductivity and superior ion selectivity by reducing the crossover of vanadium ions during the long-term operation of an all vanadium redox flow battery (VRB). The VO2+ permeability rate of SPAEK/ZrNT is 0.09 × 10−7 cm2 min−1, which is 11- and 37-fold lower compared to that of the pristine SPAEK (1.0 × 10−7 cm2 min−1) and Nafion-212 (3.3 × 10−7 cm2 min−1) membranes, respectively. The VRB assembled with a SPAEK/ZrNT composite membrane showed a significantly lower self-discharge rate, retaining an open circuit voltage of 1.3 V for 500 h, compared to the pristine SPAEK (126 h) and Nafion-212 (29 h) membranes, indicating the superior ion selectivity of the composite membrane (6.6 × 106 S min cm−3), which is an 11- and 41-fold higher ion selectivity compared to that of the pristine SPAEK and Nafion-212 membranes, respectively. The SPAEK/ZrNT composite membrane exhibits a higher coulombic efficiency (CE, 99.86%) and energy efficiency (EE, 83.82%) at 40 mA cm−2, as compared to the pristine SPAEK (CE, 97.76% and EE, 81.56%) and Nafion-212 (CE, 89.65% and EE, 75.53%) membranes. The capacity retention of the SPAEK/ZrNT composite membrane is 93%, which is much higher than that of the SPAEK (72%) and Nafion-212 (38%) membranes after 100 VRB cycles. Moreover, the VRB with the SPAEK/ZrNT composite membrane maintains a stable cycling performance at different current densities, indicating the great potential of this separator as a substitute for the commercial Nafion membrane widely used in VRBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...