Hydrogen generation properties and the hydrolysis mechanism of Zr(BH4)4·8NH3
Abstract
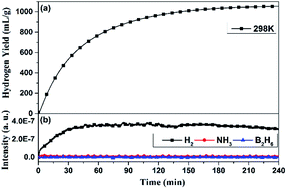
Zr(BH4)4·8NH3 is considered to be a promising solid-state hydrogen-storage material, due to its high hydrogen density and low dehydrogenation temperature. However, the release of ammonia hinders its practical applications. To further reduce the dehydrogenation temperature and suppress ammonia release, here we investigated its hydrolysis process to evaluate its hydrogen generation performance. The results showed that the hydrolysis of Zr(BH4)4·8NH3 in water can generate about 1067 mL g−1 pure hydrogen in 240 min at 298 K without the release of diborane or ammonia impurity gases. With heat-assistance, the hydrogen generation rate can be significantly enhanced, and its activation energy was calculated to be 29.38 kJ mol−1. The hydrolysis mechanism was clarified. The results demonstrate that Zr(BH4)4·8NH3 may work as one promising hydrogen generation material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...