Impact of air exposure and surface chemistry on Li–Li7La3Zr2O12 interfacial resistance†
Abstract
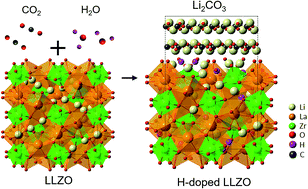
Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) is a promising solid-state electrolyte that could enable solid-state-batteries (SSB) employing metallic Li anodes. For a SSB to be viable, the stability and charge transfer kinetics at the Li–LLZO interface should foster facile plating and stripping of Li. Contrary to these goals, recent studies have reported high Li–LLZO interfacial resistance which was attributed to a contamination layer that forms upon exposure of LLZO to air. This study clarifies the mechanisms and consequences associated with air exposure of LLZO; additionally, strategies to minimize these effects are described. First-principles calculations reveal that LLZO readily reacts with humid air; the most favorable reaction pathway involves protonation of LLZO and formation of Li2CO3. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy were used to characterize the surface and subsurface chemistry of LLZO as a function of relative humidity and exposure time. Additionally, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was used to measure the Li–LLZO interfacial resistance as a function of surface contamination. These data indicate that air exposure-induced contamination impacts the interfacial resistance significantly, when exposure time exceeds 24 h. The results of this study provide valuable insight into the sensitivity of LLZO to air and how the effects of air contamination can be reversed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...