Dichlorosilane-derived nano-silicon inside hollow carbon spheres as a high-performance anode for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
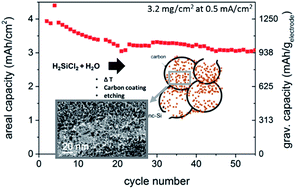
A novel and cost-effective synthesis of silicon nanocrystallites (<10 nm) sealed in hollow carbon spheres (nc-Si@HCS) is developed as a promising anode material for high-performance Li-ion batteries (LIBs). The preparation method involves dichlorosilane (H2SiCl2) as widely available feedstock, to form a hydrogen-rich polysiloxane as a precursor for the production of large quantities of silicon nanoparticles. The final electrode material is composed of agglomerated 5 nm sized silicon nanoparticles encapsulated within hollow micro-sized carbon structures. A high specific capacity of 1570 mA h gelectrode−1 at 0.25 A g−1 with a capacity retention of 65% after 250 deep discharge cycles and a reversible high areal capacity of up to 4 mA h cm−2 at a total mass loading of 3.2 mg cm−2 impressively demonstrate the excellent features of this novel anode material. We performed a detailed structural as well as electrochemical characterization in different electrolytes. Post mortem investigations help to understand the degradation mechanism in our material. The study herein heralds a new approach to structurally design advanced negative electrode materials with the potential to increase the specific energy of LIBs and to boost future electro-mobility technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...