Highly reversible sodium storage in a GeP5/C composite anode with large capacity and low voltage†
Abstract
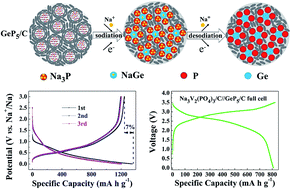
Sodium ion batteries (SIBs) are considered to be a promising alternative to lithium ion batteries because of the high abundance of sodium. However, the scarcities of suitable anode materials severely hamper the development of SIBs. Here, we synthesized a GeP5/C composite with binary sodium-reactive components on a large scale. Theoretically, it can promise a capacity of 1888 mA h g−1 or 6891 mA h cm−3, which is the best record in anodes for SIBs reported so far. In practice, the GeP5/C showed a low potential of ≈0.4 V vs. Na+/Na with a smooth charge/discharge profile. It delivered a large reversible capacity of 1250 mA h g−1 with a first coulombic efficiency of 93%. Electrochemical-mechanism studies suggested that the formation of a GeP5 phase endowed a high first coulombic efficiency and synergetic effect between the sodiation of Ge and P. This effect smoothly leveled the multistep plateaus and effectively reduced the polarization between charge/discharge. When applied to a full cell by coupling a Na3V2(PO4)3/C cathode, the assembled Na3V2(PO4)3//GeP5 full cell showed a large capacity of 800 mA h g−1 with a high average output voltage of 2.65 V. The excellent sodium-storage performances of GeP5/C will ensure commercial utilization in future SIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...