Room temperature formation of organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites: design of nanostructured and highly reactive intermediates†
Abstract
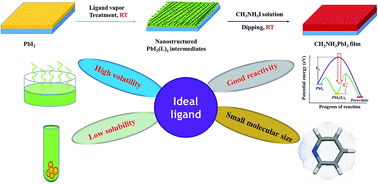
Recently, organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites have been intensively studied for use in solar cells because of their low cost and high performance. Most of the efficient perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) need layer-dependent high-temperature treatment for each layer of the multilayered structures, increasing the fabrication complexity. In addition, high temperature processes hinder their applications in flexible devices. Therefore, it is highly desirable to develop room-temperature processed methods for controllably forming perovskite films which can simplify the complicated device process and promote emerging flexible device technologies. In this work, we propose a room-temperature scheme of ligand-promoted formation of high quality perovskite films through the judicious design of nanostructured PbI2·(L)x intermediates, where L denotes the ligand. The high quality perovskite films are free of pinholes and impurities, and have high crystallinity. Using our room-temperature crystallization of perovskite films, we have fabricated highly efficient room-temperature solution-processed PVSCs with a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 17.21% (the current best PVSCs based on perovskite fabricated at room temperature have a PCE of <16%). Meanwhile, we have experimentally investigated the effects of different ligands on building the nanostructured PbI2·(L)x intermediates, and thus the purity, morphology, and optoelectronic performances of the resultant perovskite films. Through thermodynamic and kinetic studies, we theoretically study the reactivity of nanostructured PbI2·(L)x intermediates, thus elucidating the possible mechanism of ligand-promoted perovskite formation. Furthermore, with the experimental and theoretical studies, we establish the selection rules for identifying ideal ligands for the formation of high-quality perovskite films. This work offers a fundamental understanding of ligand effects on the formation of perovskite films for the future design of high-performance and low-cost perovskite-based optoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...