Promoting effects of Ce0.75Zr0.25O2 on the La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in metal–air batteries†
Abstract
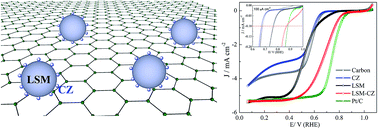
Perovskites have been proposed as one of the best oxygen reduction reaction catalysts (ORRCs) to substitute noble metals though their catalytic activity still need to be improved. It is well accepted that improving the oxygen adsorption capacity is beneficial to the catalytic activity of La1−xSrxMnO3 (LSM) perovskites. Herein, we synthesized the LSM-based composite by compositing La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 with Ce0.75Zr0.25O2 (CZ) which is used as an excellent oxygen storage material by a two-step solution method. The LSM–CZ composite is revealed as a novel electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction with the direct four-electron transfer mechanism and a positive onset potential in comparison with the commercial Pt/C catalyst. And its onset potential is almost the most positive one among those of the perovskites stemmed from LaMnO3. In addition, the stability of LSM–CZ is even superior to that of Pt/C, and LSM–CZ almost accumulates no intermediate product of HO2− (∼0.8%) after aging for 100 000 seconds. By using LSM–CZ as the ORRC, the maximum power density of the aluminum–air battery can reach 233.4 mW cm−2. Our work paves the way for the development of perovskite catalysts for energy conversion and storage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...