Potassium–sodium niobate based lead-free ceramics: novel electrical energy storage materials
Abstract
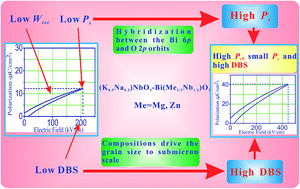
The development of lead-free bulk ceramics with high recoverable energy density (Wrec) is of decisive importance for meeting the requirements of advanced pulsed power capacitors toward miniaturization and integration. However, the Wrec (<2 J cm−3) of lead-free bulk ceramics has long been limited by their low dielectric breakdown strength (DBS < 200 kV cm−1) and small saturation polarization (Ps). In this work, a strategy (compositions control the grain size of lead-free ceramics to submicron scale to increase the DBS, and the hybridization between the Bi 6p and O 2p orbitals enhances the Ps) was proposed to improve the Wrec of lead-free ceramics. (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3–Bi(Me2/3Nb1/3)O3 solid solutions (where Me2+ = Mg and Zn) were designed for achieving large Ps, and high DBS and Wrec. As an example, (1 − x)(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3–xBi(Mg2/3Nb1/3)O3 (KNN–BMN) ceramics were prepared by using a conventional solid-state reaction process in this study. Large Ps (41 μC cm−2) and high DBS (300 kV cm−1) were obtained for 0.90KNN–0.10BMN ceramics, leading to large Wrec (4.08 J cm−3). The significantly enhanced Wrec is more than 2–3 times larger than that of other lead-free bulk ceramics. The findings in this study not only provide a design methodology for developing lead-free bulk ceramics with large Wrec but also could bring about the development of a series of KNN-based ceramics with significantly enhanced Wrec and DBS in the future. More importantly, this work opens a new research and application field (dielectric energy storage) for (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-based ceramics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...