Controlling nucleation, growth, and orientation of metal halide perovskite thin films with rationally selected additives†
Abstract
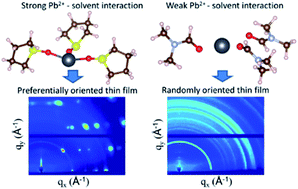
Accelerating the progress toward realizing metal halide perovskite solar cells with improved efficiency, stability and reliability requires a deeper understanding of the thin film formation processes. This paper investigates the impact of rationally selected chemical additives in precursor solutions on the nucleation and growth of metal halide perovskite thin films. Computational screening was performed to guide the selection of tetrahydrothiophene oxide as an additive with stronger solvation efficacy than all other commonly used solvents. In situ grazing incidence X-ray diffraction measurements show that the additives suppress the formation of homogeneous nuclei as well as crystalline intermediate structures. Instead, heterogeneous nucleation on the substrate surface and growth of a thin film with a strongly preferential crystallographic orientation occur directly from the precursor solution. Density functional theory calculations show that the crystallographic orientation of the thin films can be tuned by altering the surface energies with the chemical additives. The crystallographic orientation of the thin films is found to have a significant impact on the open circuit voltage of solar cell devices, highlighting the importance of controlling the metal halide perovskite thin film orientation for improved solar cell efficiency.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...